Next in this tutorial will be shown some examples of english grammar structure:
Contents you will find
In this blog you will find several topics which are frequently used in any situation of your life, starting from the basics, for instance the vocabulary needed before you may start using the grammatical structures, it begins with: The colors and the ordinal and cardinal numbers,days of the week, months of the year, parts of the body, animals, transport means, jobs and occupations, food in general, clothing, among others, in a medium level of learning the student find throughout the blog topics of interest as verb tenses ( past, present and future, the conjugation of "to be" verb, regular and irregular verbs, false cognates, phrasal verbs, contable and uncountable nouns, general expressions as greetings, the WH questions, nouns, adjectives, adverbs,
LIST OF THE ORDINAL AND CARDINAL NUMBERS

LIST OF THE BASIC COLORS

DAYS OF THE WEEK

MONTHS OF THE YEAR
PARTS OF THE BODY

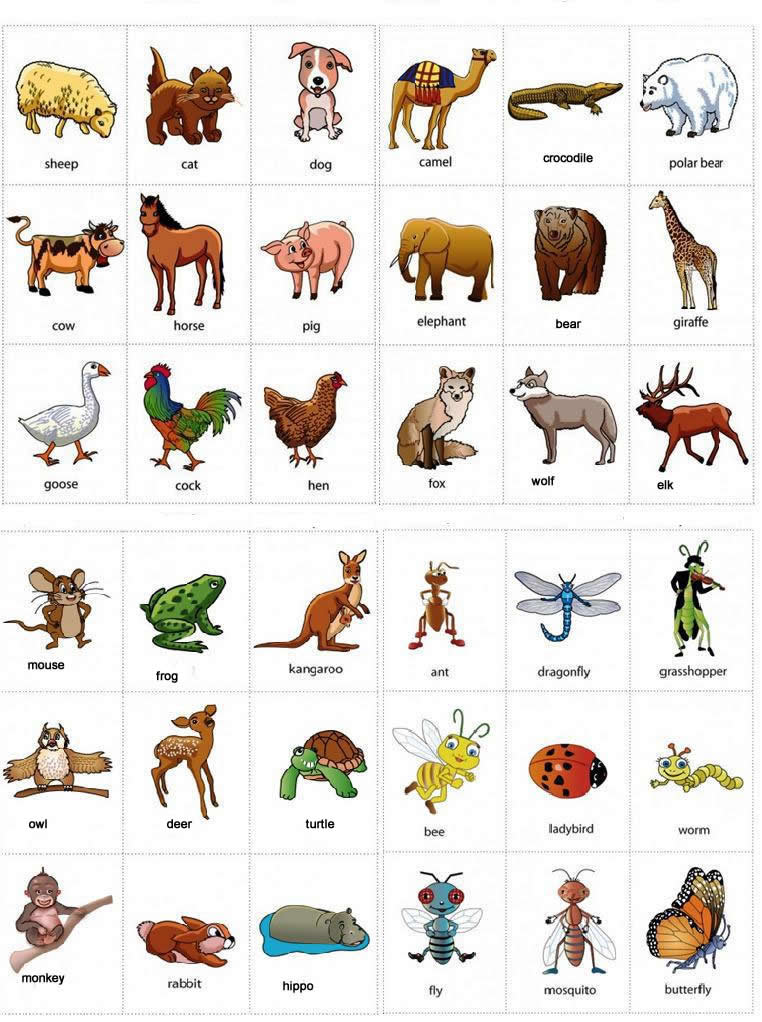
ANIMALS
MEANS OF TRANSPORT

JOBS AND OCCUPATION

CLOTHES

FOOD

FURNITURE

PARTS OF HOUSE
WEATHER CONDITIONS
STATIONS

PLACES

TOOLS

ELECTRONICS

MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS

KARAOKE: this video is for improve the speaking and listening
Incomplete lyrics of the rolling in the deep
Complete the lyrics
There's
a fire starting in my _________ ,
Reaching
a fever pitch
It's
bringing me out the dark.
Finally,
I can see you __________clear.
Go
ahead and sell me out
And
I'll lay your ship bare.
See
how I ____________ with every piece of you.
Don't
underestimate
The
things that I will do.
There's
a fire starting in my ____________ ,
Reaching
a fever pitch,
And
it's bringing me out the dark.
The
_________of your love remind me of us.
They
keep me thinking that we almost had it all.
The
___________of your love, they leave me breathless.
I
can't help feeling
We
could have had it all.
Rolling
in the deep.
You
had my heart inside of your ____________.
And
you played it to the beat.
Baby,
I have no story to be _____________
But
I've heard one on you.
And
I'm gonna make your head ___________.
Think
of me in the depths of your despair.
Make
a home down there,
As
mine sure won't be ___________.
The
__________ of your love remind me of us.
They
keep me thinking that we almost had it all.
The
_________ of your love, they leave me breathless.
I
can't help feeling
We
could have had it all.
Rolling
in the deep.
You
had my heart inside of your ____________.
And
you played it to the beat.
We
could have had it all.
Rolling
in the deep.
You
had my heart inside of your ___________.
But
you played it with a beating.
Throw
your _______ through every open door.
Count
your blessings to find what you look for.
Turn
my sorrow into treasured __________.
You'll
pay me back in kind and reap just what you ______.
We
could have had it all.
We
could have had it all.
It
all, it all, it all.
We
could have had it all.
Rolling
in the deep.
You
had my heart inside of your _________.
And
you played it to the beat.
We
could have had it all.
Rolling
in the deep.
You
had my heart inside of your _________.
But
you played it,
You
played it,
You played it,
You played it to the
beat.
Complete the lyrics
I close my eyes only for a __________, and the moment's gone
All my ______ pass before my eyes, a __________
Dust in the _______, all they are is _______ in the wind
Same old song, just a drop of ______ in an endless ______
All we do crumbles to the _______, though we refuse to see
Dust in the wind, all we are is dust in the wind
Now, don't _____ on, nothing lasts _______ but the earth and sky
It slips ______, and all your money won't _______ minute buy
Dust in the wind, all we are is dust in the wind (all we are is dust in the wind)
Dust in the wind (everything is dust in the wind), everything is dust in the wind (the wind)
Dust in the _______, all they are is _______ in the wind
Same old song, just a drop of ______ in an endless ______
All we do crumbles to the _______, though we refuse to see
Dust in the wind, all we are is dust in the wind
Now, don't _____ on, nothing lasts _______ but the earth and sky
It slips ______, and all your money won't _______ minute buy
Dust in the wind, all we are is dust in the wind (all we are is dust in the wind)
Dust in the wind (everything is dust in the wind), everything is dust in the wind (the wind)
Verb tenses are tools that English speakers use to express time in their language. You may find that many English tenses do not have direct translations in your language. That is not a problem. By studying this verb tense explanation, you will learn to think like a native English speaker. If you prefer to use many verb tenses in many situations or learn their structures step by step, then you will find many of the known tenses so far, and see what are their purpose.
Simple Present
FORM
[VERB] + s/es in third person
Examples:
- You speak English.
- Do you speak English?
- You do not speak English.
USE 1 Repeated Actions

Use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do.
Examples:
- I play tennis.
- She does not play tennis.
- Does he play tennis?
- The train leaves every morning at 8 AM.
- The train does not leave at 9 AM.
- When does the train usually leave?
- She always forgets her purse.
- He never forgets his wallet.
- Every twelve months, the Earth circles the Sun.
- Does the Sun circle the Earth?
USE 2 Facts or Generalizations

The Simple Present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true now, and will be true in the future. It is not important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is also used to make generalizations about people or things.
Examples:
- Cats like milk.
- Birds do not like milk.
- Do pigs like milk?
- California is in America.
- California is not in the United Kingdom.
- Windows are made of glass.
- Windows are not made of wood.
- New York is a small city. It is not important that this fact is untrue.
USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future

Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events as well.
Examples:
- The train leaves tonight at 6 PM.
- The bus does not arrive at 11 AM, it arrives at 11 PM.
- When do we board the plane?
- The party starts at 8 o'clock.
- When does class begin tomorrow?
USE 4 Now (Non-Continuous Verbs)

Speakers sometimes use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is happening or is not happening now. This can only be done with Non-Continuous Verbs and certain Mixed Verbs.
Examples:
- I am here now.
- She is not here now.
- He needs help right now.
- He does not need help now.
- He has his passport in his hand.
- Do you have your passport with you?
Simple Past
FORM
[VERB+ed] or irregular verbs
Examples:
Complete List of Simple Past Forms- You called Debbie.
- Did you call Debbie?
- You did not call Debbie.
USE 1 Completed Action in the Past

Use the Simple Past to express the idea that an action started and finished at a specific time in the past. Sometimes, the speaker may not actually mention the specific time, but they do have one specific time in mind.
Examples:
- I saw a movie yesterday.
- I didn't see a play yesterday.
- Last year, I traveled to Japan.
- Last year, I didn't travel to Korea.
- Did you have dinner last night?
- She washed her car.
- He didn't wash his car.
USE 2 A Series of Completed Actions

We use the Simple Past to list a series of completed actions in the past. These actions happen 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and so on.
Examples:
- I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim.
- He arrived from the airport at 8:00, checked into the hotel at 9:00, and met the others at 10:00.
- Did you add flour, pour in the milk, and then add the eggs?
USE 3 Duration in Past

The Simple Past can be used with a duration which starts and stops in the past. A duration is a longer action often indicated by expressions such as: for two years, for five minutes, all day, all year, etc.
Examples:
- I lived in Brazil for two years.
- Shauna studied Japanese for five years.
- They sat at the beach all day.
- They did not stay at the party the entire time.
- We talked on the phone for thirty minutes.
- A: How long did you wait for them?
B: We waited for one hour.
USE 4 Habits in the Past

The Simple Past can also be used to describe a habit which stopped in the past. It can have the same meaning as "used to." To make it clear that we are talking about a habit, we often add expressions such as: always, often, usually, never, when I was a child, when I was younger, etc.
Examples:
- I studied French when I was a child.
- He played the violin.
- He didn't play the piano.
- Did you play a musical instrument when you were a kid?
- She worked at the movie theater after school.
- They never went to school, they always skipped class.
USE 5 Past Facts or Generalizations

The Simple Past can also be used to describe past facts or generalizations which are no longer true. As in USE 4 above, this use of the Simple Past is quite similar to the expression "used to."
Examples:



- She was shy as a child, but now she is very outgoing.
- He didn't like tomatoes before.
- Did you live in Texas when you were a kid?
- People paid much more to make cell phone calls in the past.
- Simple Future
-
Simple Future has two different forms in English: "will" and "be going to." Although the two forms can sometimes be used interchangeably, they often express two very different meanings. These different meanings might seem too abstract at first, but with time and practice, the differences will become clear. Both "will" and "be going to" refer to a specific time in the future.

FORM Will
[will + verb]
Examples:
- You will help him later.
- Will you help him later?
- You will not help him later.
FORM Be Going To
[am/is/are + going to + verb]
Examples:Complete List of Simple Future Forms
- You are going to meet Jane tonight.
- Are you going to meet Jane tonight?
- You are not going to meet Jane tonight.
USE 1 "Will" to Express a Voluntary Action
"Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do something for us. Similarly, we use "will not" or "won't" when we refuse to voluntarily do something.
Examples:
- I will send you the information when I get it.
- I will translate the email, so Mr. Smith can read it.
- Will you help me move this heavy table?
- Will you make dinner?
- I will not do your homework for you.
- I won't do all the housework myself!
- A: I'm really hungry.
B: I'll make some sandwiches. - A: I'm so tired. I'm about to fall asleep.
B: I'll get you some coffee. - A: The phone is ringing.
B: I'll get it.
USE 2 "Will" to Express a Promise
"Will" is usually used in promises.
Examples:
- I will call you when I arrive.
- If I am elected President of the United States, I will make sure everyone has access to inexpensive health insurance.
- I promise I will not tell him about the surprise party.
- Don't worry, I'll be careful.
- I won't tell anyone your secret.
USE 3 "Be going to" to Express a Plan
"Be going to" expresses that something is a plan. It expresses the idea that a person intends to do something in the future. It does not matter whether the plan is realistic or not.
Examples:
- He is going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
- She is not going to spend her vacation in Hawaii.
- A: When are we going to meet each other tonight?
B: We are going to meet at 6 PM. - I'm going to be an actor when I grow up.
- Michelle is going to begin medical school next year.
- They are going to drive all the way to Alaska.
- Who are you going to invite to the party?
- A: Who is going to make John's birthday cake?
B: Sue is going to make John's birthday cake.
USE 4 "Will" or "Be Going to" to Express a Prediction
Both "will" and "be going to" can express the idea of a general prediction about the future. Predictions are guesses about what might happen in the future. In "prediction" sentences, the subject usually has little control over the future and therefore USES 1-3 do not apply. In the following examples, there is no difference in meaning.
Examples:
- The year 2222 will be a very interesting year.
- The year 2222 is going to be a very interesting year.
- John Smith will be the next President.
- John Smith is going to be the next President.
- The movie "Zenith" will win several Academy Awards.
- The movie "Zenith" is going to win several Academy Awards.
- The conditionals
What are conditionals in English grammar? Sometimes we call them 'if clauses'. They describe the result of something that might happen (in the present or future) or might have happened but didn't (in the past) . They are made using different English verb tenses. There are four kinds:- The Zero Conditional:
(if + present simple, ... present simple)
If you heat water to 100 degrees, it boils. - The First Conditional:
(if + present simple, ... will + infinitive)
If it rains tomorrow, we'll go to the cinema. - The Second Conditional:
(if + past simple, ... would + infinitive)
If I had a lot of money, I would travel around the world. - The Third Conditional
(if + past perfect, ... would + have + past participle)
If I had gone to bed early, I would have caught the train. Adjectives
An adjective is a word that tells us more about a noun. (By "noun" we include pronouns and noun phrases.)An adjective "qualifies" or "modifies" a noun (a big dog).Adjectives can be used before a noun (I like Chinese food) or after certain verbs (It is hard).We can often use two or more adjectives together (a beautiful young French lady).It is sometimes said that the adjective is the enemy of the noun. This is because, very often, if we use the precise noun we don't need an adjective. For example, instead of saying "a large, impressive house" (2 adjectives + 1 noun) we could simply say "a mansion" (1 noun).
L'objectif principal de ce blog est de promouvoir l'apprentissage de l'autonomie en anglais, français et allemand, dans cet espace les étudiants peuvent publier et partager des contenus différents sur les connaissances qu'ils ont en anglais pour aider d'autres personnes à augmenter leur sagesse en anglais qui est Divisé par plusieurs thèmes, par exemple: (vidéos, didacticiels, chansons, structure grammaticale de cette langue donnant quelques exercices pour pratiquer les choses apprises).
Ensuite dans ce tutoriel seront montrés quelques exemples de structure grammaticale Français:
Contenu que vous trouverez
Dans ce blog vous trouverez plusieurs sujets qui sont fréquemment utilisés dans n'importe quelle situation de votre vie, à partir des bases, par exemple le vocabulaire nécessaire avant que vous puissiez commencer à utiliser les structures grammaticales, il commence par: Les couleurs et les nombres ordinaux et cardinaux , Les jours de la semaine, les mois de l'année, les parties du corps, les animaux, les moyens de transport, les emplois et les occupations, la nourriture en général, les vêtements, entre autres, dans un niveau d'apprentissage moyen que l'étudiant trouve tout au long du blog Verbes verbaux, verbes réguliers et irréguliers, faux cognats, verbes phrasés, noms contables et innombrables, expressions générales comme salutations, questions WH, noms, adjectifs, adverbes,
LISTE DES NOMBRES ORDINAIRES ET CARDINAUX


LISTE DES COLEURS

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario